what is normal sugar levels in blood Normally, your pancreas releases insulin normal blood sugar level when your blood sugar, or “blood glucose,” gets high after a meal, for example. That signals your body to absorb glucose until levels get back to normal.
But if you have diabetes, your body doesn’t make insulin (type 1 diabetes) or doesn’t respond to it normally (type 2 diabetes). That can leave your blood sugar too high for too long. Over time, that can damage nerves and blood vessels and lead to heart disease and other problems.
If you have diabetes, your doctor may ask you to keep track of your blood sugar by testing it at home with a special device called a blood glucose monitor or home blood sugar meter. It takes a small sample of blood, usually from the tip of your finger, and measures the amount of glucose in it.
Follow your doctor’s instructions about the best way to use your device.
Your doctor will tell you when and how to test your blood sugar. Each time you do it, log it in a notebook or online tool or in an app. The time of day, recent activity, your last meal, and other things can all affect whether a reading will be of concern to your doctor. So try to log relevant information lik

- What medication and dosage you took
- What you ate, when you ate, or whether you were fasting
- How much, how intense, and what kind of exercise you were doing, if any
What Is a Normal Blood Sugar Level?
Blood glucose levels are the amount of glucose, or sugar, that someone has in their blood at any given time. Having high or low blood sugar levels could indicate an underlying health condition that may require medical attention. Use this overview of normal blood glucose levels to understand what your blood sugar levels mean.
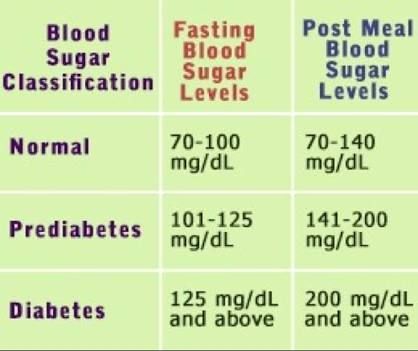
Fasting normal blood sugar
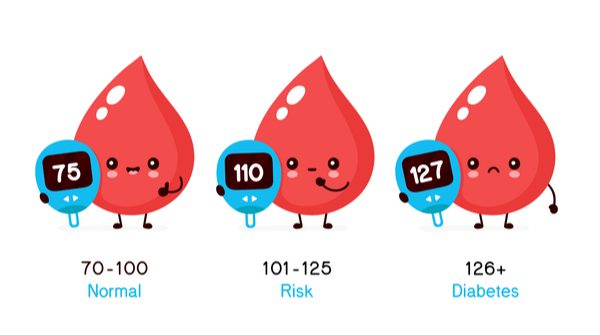
Normal for person without diabetes: 70–99 mg/dl (3.9–5.5 mmol/L)
blood sugar Normal 2 hours after meals
Normal for person without diabetes: Less than 140 mg/dl (7.8 mmol/L)
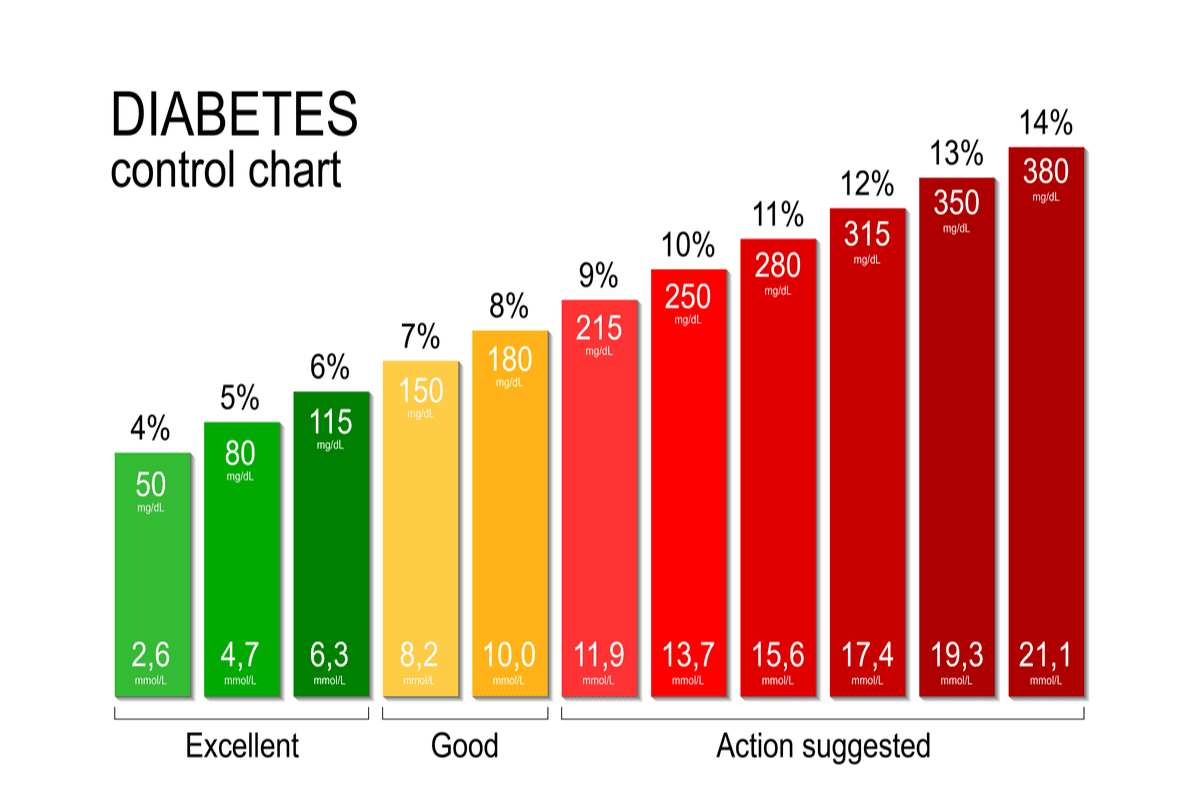
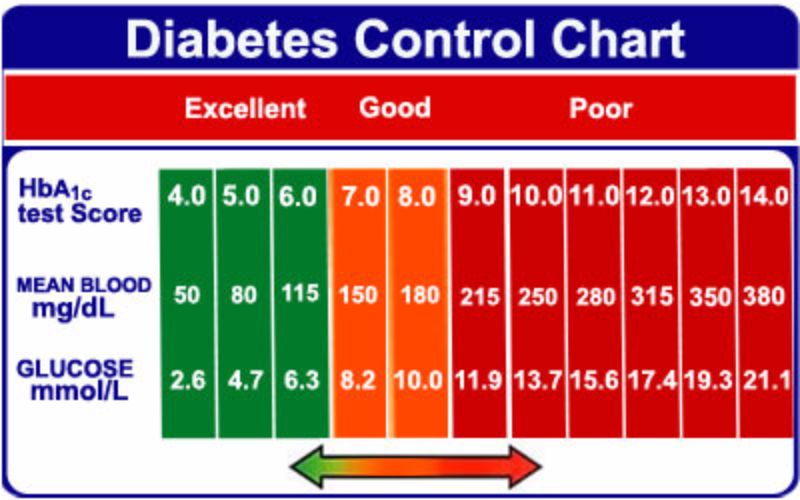
HbA1c
Normal for person without diabetes: Less than 5.7%
Blood sugar levels and diabetes
If you have diabetes, you may be wondering (or, have wondered at some point) what your blood glucose (sugar) “should” be. Hopefully your doctor, nurse practitioner, physician’s assistant or whoever diagnosed you has given you answers to that question. Unfortunately, though, not everyone is given glucose goals. Or in some cases, it may have been a long time ago, and they’ve since been forgotten. No worries — we’ll go over all that!
What is blood glucose, anyway?
Blood glucose, or sugar, is sugar that is in your blood (easy enough!). It comes from the food that you eat — foods that contain carbohydrate, such as bread, pasta, and fruit are the main contributors to blood glucose. The cells in our bodies need glucose for energy — and we all need energy to move, think, learn, and breathe. The brain, which is the command center, uses about half of all the energy from glucose in the body.
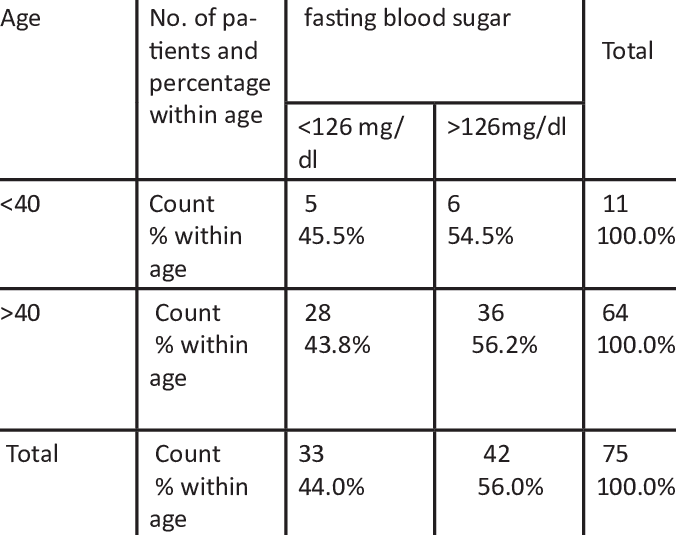
What are normal blood sugar levels in healthy individuals?
Blood sugar levels can either be normal, high, or low, depending on how much glucose someone has in their bloodstream. Glucose is a simple sugar that’s present in the bloodstream at all times. Blood glucose levels can be measured at any time, for example, when someone fasts (in the morning upon awakening), before they eat, or after they’ve eaten. A normal blood glucose level for adults, without diabetes, who haven’t eaten for at least eight hours (fasting) is less than 100 mg/dL. A normal blood glucose level for adults, without diabetes, two hours after eating, is 90 to 110 mg/dL.
Many factors affect blood sugar levels throughout the day:
- Type of food consumed, how much, and when
- Physical activity
- Medications
- Medical conditions
- Age
- Stress
- Dehydration
- Illness
- Menstrual periods
- Alcohol
An ideal blood sugar level for anyone without diabetes or prediabetes, regardless of age, in the morning should be less than 100 mg/dL. Remember, blood sugar levels can fluctuate throughout the day as a result of the factors previously mentioned.

Types of diabetes
Before going into blood sugar levels, here is a brief overview of the different types of diabetes.
Type 1 diabetes
1 Type diabetes is caused when the immune system attacks cells in the pancreas. Type 1 diabetes is not caused by diet or lifestyle. It is known as insulin-dependent diabetes, meaning that insulin is required in order to live. Type diabetes usually occurs in children and young adults, but can occur at any age. There is no way to prevent type 1 diabetes, and there is currently no cure.

People with type 1 diabetes need to inject insulin—or use insulin via a pump—to control blood sugar levels. Although it is important for everyone to have a healthy diet and exercise, people with type 1 diabetes will need insulin every day (regardless of what they eat) to keep blood sugar levels in range.
People with type 1 diabetes use several kinds of insulin. For example, basal insulin (which is injected once or twice daily or given through the pump) holds blood sugar steady under fasting conditions. A fast-acting insulin is also used, to help the body process foods, and to bring down blood sugar levels when necessary.
Type 2 diabetes
Type 2 diabetes is more common in adults over age 45, but can occur in chidren and younger adults. In type 2 diabetes, cells do not respond properly to insulin. This is called insulin resistance. The pancreas has to work harder to make more insulin and eventually can’t keep up and blood sugar rises.
There are certain risk factors for type 2 diabetes.
For people with type 2 diabetes, diet, exercise, and oral medications are used to control blood sugar. Sometimes, injectable medications (insulin—or other injectable medicines that are not insulin but help lower blood sugar) are used as well.
Gestational diabetes
Gestational diabetes sometimes occurs in pregnant women. Having gestational diabetes increases the risk of your baby having health problems. In most cases, gestational diabetes goes away after the baby is born. However, you will have a higher risk of getting type 2 diabetes later in life. Also, your baby is more likely to have obesity during childhood and teenage years, and is more likely to develop type 2 diabetes later in life. Women with gestational diabetes will be instructed to make dietary changes and exercise more, and they will be closely monitored. In some cases, insulin or diabetes medication (such as metformin) may be needed to help lower blood sugar levels.
Prediabetes
People with prediabetes have blood sugar levels that are higher than normal but not high enough to be diagnosed with type 2 diabetes. Having prediabetes increases the risk of having type 2 diabetes, heart disease, and stroke.
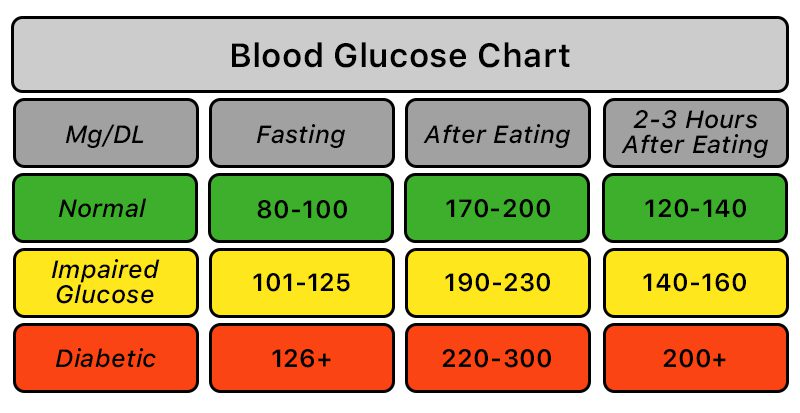
Blood sugar level charts for those with diabetes
Normal blood sugar levels, for those with diabetes, will vary depending on someone’s age and the time of day. For example, when fasting, blood sugar levels are often in the target goal range. The type of food eaten will impact blood sugar levels in different ways. A meal with a lot of carbohydrates (for example, cereal and waffles) will raise blood sugar quicker than a meal that contains carbohydrates, protein, and fat (for example, a hamburger and french fries). Blood sugar will rise after a meal, but will start to return to normal levels in several hours.
Let’s take a look at what blood sugar levels should be, in those with diabetes, based on their age.
When things go awry
When we eat food, the pancreas (an organ that sits between the stomach and the spine) goes to work, releasing enzymes that help to break down food and hormones that help the body handle the influx of glucose. One of these hormones is insulin, and it plays a key role in managing glucose levels in the blood.
And here is where things can go wrong. If the pancreas doesn’t make enough insulin — or stops making it altogether, in the case of type 1 diabetes — glucose levels in the blood can rise too high. Another scenario is that the pancreas makes enough insulin but the cells have trouble using it properly, causing blood glucose levels to rise. This is called insulin resistance and is the hallmark of type 2 diabetes.
In the short term, high blood glucose levels can make you feel downright bad. Thirst, frequent trips to the bathroom, fatigue, and weight loss are all symptoms of high blood glucose (hyperglycemia). If not treated, more serious issues can occur, such as diabetic ketoacidosis (DKA). Chronic high blood glucose levels can lead to complications such as heart, kidney and eye disease, as well as nerve damage. So, it’s all about the blood glucose.
How do you know what your blood glucose level is?
For the most part, you can’t “feel” what your blood glucose level is — unless it’s fairly high or it’s low. You may not even always have symptoms of either high or low blood glucose; in fact, many people with type 2 diabetes don’t have the usual symptoms of high blood glucose, and for this reason, it’s not uncommon for people to go undiagnosed for many years.
The best way to know your blood glucose level is to check it with a glucose meter. This means doing a finger-stick with a lancet and getting a drop of blood onto a test strip, then inserting the strip into the meter for a reading. Your doctor may be able to give you a meter free of charge, but you’ll likely need to pay for test strips and lancets. But check with your health plan, as there are likely one or two “preferred” meters that they want you to use.
Another way to know what your glucose levels are up to is to use a continuous glucose monitor, or CGM. Which reads glucose in the interstitial fluid (the fluid between cells) about every five minutes. Continuous glucose monitoring is expensive and may or may not be covered by your health plan.
Low blood sugar symptoms
Low blood sugar, also called hypoglycemia, is what happens when blood glucose levels drop too low. People who take insulin may have low blood sugar if they take too much insulin or mistime the insulin dose in relation to food, or if they exercise more than usual when there is fast-acting insulin “on board” (in the body).
Your healthcare provider will tell you when and how to check blood sugar, and when and how to treat low blood sugar. A low blood sugar is generally considered to be less than 70 mg/dL. A dangerously low blood sugar is below 54 mg/dL.
Low blood sugar can also be caused by many things including certain medications or combinations of medications, alcohol, endocrine disorders, eating disorders, and disorders of the liver, kidneys, or heart.
Here are some of the most common symptoms that someone with low blood sugar might experience:
- Lightheadedness
- Dizziness
- Confusion
- Irritability
- Shakiness
- Nervousness
- Anxiety
- Sweating
- Clamminess
- Having a fast heart rate
- Pale skin
- Hunger
- Sleepiness
- Fainting
- Tingling lips
Treatment
Depending on what type of diabetes you have, blood sugar monitoring, insulin and oral drugs may be part of your treatment. Eating a healthy diet, staying at a healthy weight and getting regular physical activity also are important parts of managing diabetes.
Treatments for all types of diabetes
An important part of managing diabetes — as well as your overall health — is keeping a healthy weight through a healthy diet and exercise plan:
-
Healthy eating.
There’s no specific diabetes diet. You’ll need to focus your diet on more fruits, vegetables, lean proteins and whole grains. These are foods that are high in nutrition and fiber and low in fat and calories. You’ll also cut down on saturated fats, refined carbohydrates and sweets. In fact, it’s the best eating plan for the entire family. Sugary foods are OK once in a while. They must be counted as part of your meal plan.
Understanding what and how much to eat can be a challenge. A registered dietitian can help you create a meal plan that fits your health goals, food preferences and lifestyle. This will likely include carbohydrate counting, especially if you have type 1 diabetes or use insulin as part of your treatment.
-
Physical activity.
Everyone needs regular aerobic activity. This includes people who have diabetes. Physical activity lowers your blood sugar level by moving sugar into your cells, where it’s used for energy. Physical activity also makes your body more sensitive to insulin. That means your body needs less insulin to transport sugar to your cells.
Get your provider’s OK to exercise. Then choose activities you enjoy, such as walking, swimming or biking. What’s most important is making physical activity part of your daily routine.
Also Read :What Foods Increase Hemoglobin | Rich Hemoglobin Food
Aim for at least 30 minutes or more of moderate physical activity most days of the week, or at least 150 minutes of moderate physical activity a week. Bouts of activity can be a few minutes during the day. If you haven’t been active for a while, start slowly and build up slowly. Also avoid sitting for too long. Try to get up and move if you’ve been sitting for more than 30 minutes.
Treatments for type 1 and type 2 diabetes
Treatment for type 1 diabetes involves insulin injections or the use of an insulin pump, frequent blood sugar checks, and carbohydrate counting. For some people with type 1 diabetes, pancreas transplant or islet cell transplant may be an option.
Treatment of type 2 diabetes mostly involves lifestyle changes, monitoring of your blood sugar, along with oral diabetes drugs, insulin or both.
Monitoring your blood sugar
Depending on your treatment plan, you may check and record your blood sugar as many as four times a day or more often if you’re taking insulin. Careful monitoring is the only way to make sure that your blood sugar level remains within your target range. People with type 2 diabetes who aren’t taking insulin generally check their blood sugar much less often.
People who receive insulin therapy also may choose to monitor their blood sugar levels with a continuous glucose monitor. Although this technology hasn’t yet completely replaced the glucose meter, it can lower the number of fingersticks necessary to check blood sugar and provide important information about trends in blood sugar levels.
Even with careful management, blood sugar levels can sometimes change unpredictably. With help from your diabetes treatment team, you’ll learn how your blood sugar level changes in response to food, physical activity, medications, illness, alcohol and stress. For women, you’ll learn how your blood sugar level changes in response to changes in hormone levels.
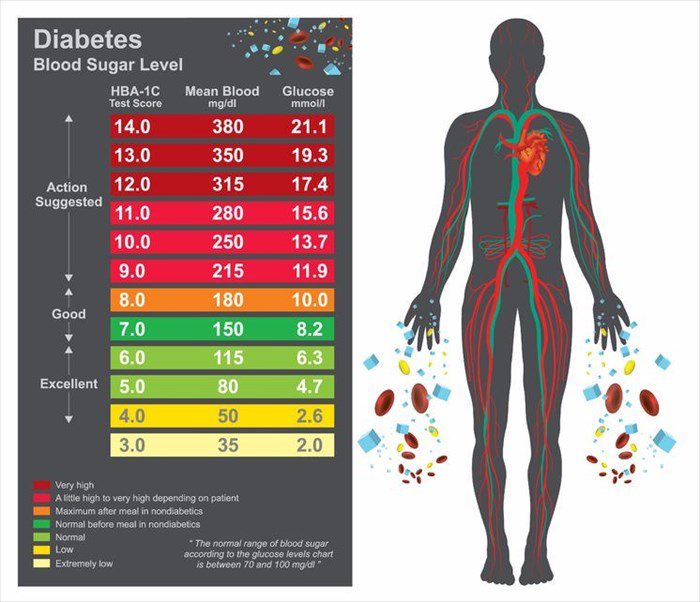
Besides daily blood sugar monitoring, your provider will likely recommend regular A1C testing to measure your average blood sugar level for the past 2 to 3 months.
Compared with repeated daily blood sugar tests, A1C testing shows better how well your diabetes treatment plan is working overall. A higher A1C level may signal the need for a change in your oral drugs, insulin regimen or meal plan.
Your target A1C goal may vary depending on your age and various other factors, such as other medical conditions you may have or your ability to feel when your blood sugar is low. However, for most people with diabetes, the American Diabetes Association recommends an A1C of below 7%. Ask your provider what your A1C target is.
Insulin
People with type 1 diabetes need insulin therapy to survive. Many people with type 2 diabetes or gestational diabetes also need insulin therapy.
Many types of insulin are available, including short-acting (regular insulin), rapid-acting insulin, long-acting insulin and intermediate options. Depending on your needs, your provider may prescribe a mixture of insulin types to use during the day and night.
Insulin can’t take orally to lower blood sugar because stomach enzymes interfere with insulin’s action. Insulin is often injected using a fine needle and syringe or an insulin pen — a device that looks like a large ink pen.
An insulin pump also may be an option. The pump is a device about the size of small cellphone worn on the outside of your body. A tube connects the reservoir of insulin to a tube (catheter) that’s insert under the skin of your abdomen.
Also Read :What is 1 Feet in Cm – Feet to Centimeter Calculator
High blood sugar symptoms
Hyperglycemia is the medical term for high blood sugar. Hyperglycemia happens when the body doesn’t have enough insulin. normal blood sugar level or when it can’t use insulin correctly. Many things can cause high blood glucose levels like Type 1 diabetes, Type 2 diabetes, stress, illness, or the dawn phenomenon. If you have hyperglycemia or suspect you may have it, talking with a healthcare provider is always a good idea. A doctor can help you determine what’s causing your high blood sugar levels and help you lower it to a healthy range.
Here are some of the most common symptoms that may indicate hyperglycemia:
- Fatigue
- Increased thirst and hunger
- Frequent urination
- Weight loss
- Headaches
- Blurred vision
- Difficulty concentrating
Here are some lifestyle changes and medical treatments that can help treat hyperglycemia:
- Eat whole, low sugar foods that are minimally process to keep the amount of glucose in the body at a lower level.
- Only exercise if there are no ketones present in the bloodstream. You can check if you have ketones with a urine test or blood glucose meter.
- Drink lots of water to help your body get rid of sugar in your urine.
- Use your insulin to correct high blood sugar levels. Your healthcare provider can help you determine the correct insulin dosages to help reduce elevated blood sugar levels.
- Take medications as per your healthcare provider’s recommendations. Some of the most commonly prescribed medications for high blood sugar are Metformin HCl, Glipizide, and Glyburide.






